FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCEIncontinence Incontinence is involuntry leakage of urine seen in both men and women in the elderly age group. The common problem in women are either urge incontinence (inability to hold urine till the toilet), stress incontinence where leakage occurs during a strenous work or cough/sneezing. In both the cases the treatment depends upon the severiety of the problem. For mild cases medical treatment with drugs like oxybutinin or other anti cholinergics can be tried. For more difficult cases of urge incontinence newer treatments like Botox injection into the bladder are available. Surgeries are rarely needed for urge incontinence and are usually preferred in the children and young adults. Bothersome stress incontinence in both men and women can be treated by using urethral slings placed at surgery. Artificial urethral sphincter is also available but involves complicated surgery and high cost. Milder cases of stress incontinence can be treated with medicines like Duloxitene. In women very often stress incontinence treatment also involves surgical corrections of associated prolapse of pelvic organs. These procedures carry success rate of 80-90%. FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE Incontinence is involuntary loss of urine. Urinary incontinence is a significant health problem with considerable social and economical impact on individual and society.In young women, the prevalence of incontinence is usually low; but prevalence peaks around menopause, with steady rise thereafter into later life. Although the prevalence of stress and mixed (stress and urge ) incontinence is higher than urge incontinence, the latter is more likely to require treatment. Signs and Symptoms In women moderate and severe bother have a prevalence ranging from about 3% to 17 . Types of incontinence
Stress Incontinence Stress incontinence is sudden leakage of urine with coughing, sneezing or exercise. It is commomly seen in women after childbirth or menopause. Commonly due to weakness of pelvic floor muscle, urinary sphincter (valve) of combinatoin of both. 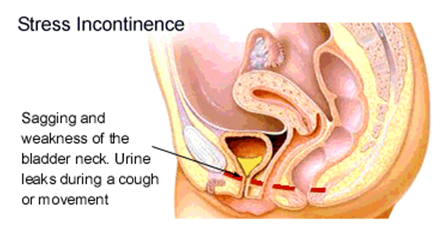
Treatment
Pelvic floor exercise is done to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. It has to be done regularly and several times a day. It takes only few minutes and results are expected only after 6 months if they are done regularly. Pelvic floor exercises along with medications have produced good results in patients with mild to moderate incontinence. 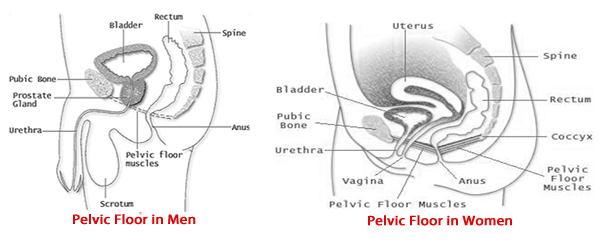

|

+91 - 95661 39630
+91 - 94441 68963



